SCIENTIFIC PROGRESS ANALYSIS AND MEASUREMENT
This project investigates methods to analyze and measure scientific progress within and across research domains. By leveraging techniques such as bibliometric analysis, citation network modeling, topic evolution tracking, and natural language processing, we aim to map the development of knowledge, identify emerging trends, and highlight influential work in a given field. Our goal is to provide researchers, institutions, and policymakers with tools and insights that support strategic planning, uncover research gaps, and enhance understanding of how science evolves over time. This project contributes to the broader goal of making the science of science more accessible, transparent, and actionable through interactive, data-driven approaches. .
SUBPROJECTS
AutoLit
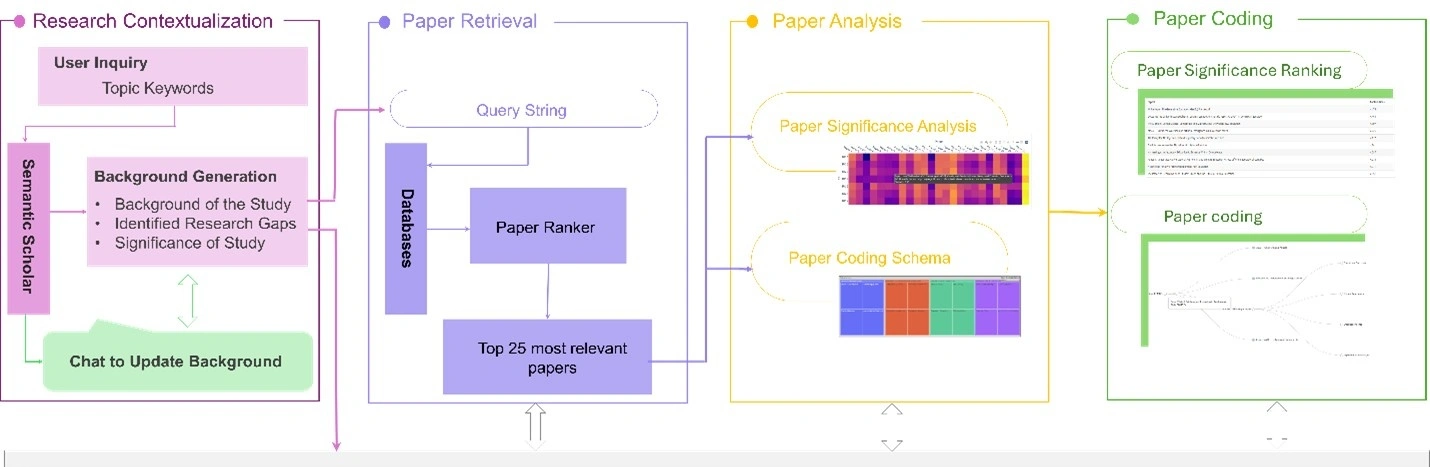
This study introduces AutoLit, a human-centered, interactive platform powered by large language models (LLMs) for supporting researchers in demystifying each step in conducting SLRs. AutoLit is structured around 4 integrated modules to facilitate the entire review process: Research Contextualization Module for generating research background and constructing research questions; Paper Retrieval Module for designing query strings and retrieving relevant papers; Paper Analysis Module for analyzing the semantic correlations among retrieved papers and research questions to highlight the most significant papers; and Paper Coding Module for generating coding schema to systematically extract insights for addressing each individual research question.
SmartRead
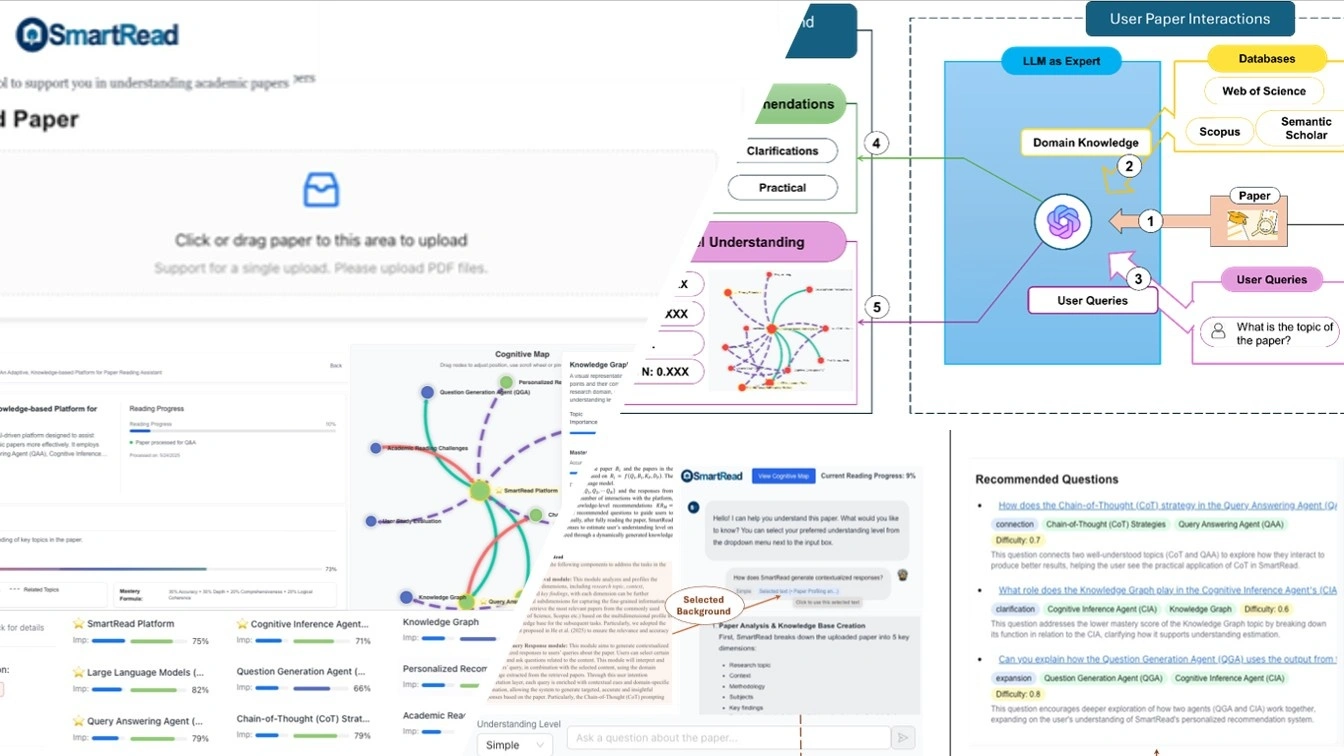
This study introduces SmartRead, a paper reading assistance platform that estimates users’ knowledge and provides individualized reading guidance with the considerations of the broader knowledge in the field. Specifically, we first fine-tune the LLMs with extensive, domain-specific contents, enabling them to generate contextualized, accurate responses to users’ queries related to a specific paper. Additionally, the platform dynamically estimates users’ domain knowledge and research interests in the real-time, offering personalized, knowledge-level recommendations to guide them toward deeper and more meaningful exploration. To further support users’ research and understanding in the field, the platform constructs a knowledge graph to visually represent users’ understanding levels on each key knowledge component in the broader research field. This visual representation helps users clearly identify their current strengths and knowledge gaps, guiding targeted exploration, deeper engagement, and effective planning for the following research.
Du, H., Xing, W., Pei, B., Zeng, Y., Lu, J., & Zhang, Y. (2023). "A Descriptive and Historical Review of STEM + C Research: A Bibliometric Study." In: Uhomoibhi, J. (eds) Computer Supported Education. CSEDU 2022. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1817. Springer, Cham.
View Paper →Pei, B., Xing, W., & Wang, M. (2021). "Academic development of multimodal learning analytics: a bibliometric analysis." Interactive Learning Environments, 31(6), 3543–3561.
View Paper →Sun, X., Sharma, P., & Pei, B. (2025). "AutoLit: An LLM-driven Interactive Platform for Powering Systematic Literature Review." In R. Jake Cohen (Ed.), Proceedings of Society for Information Technology & Teacher Education International Conference (pp. 880-886).
View Paper →